SubInfo: Collecting Participant Information¶
Overview¶
The SubInfo class provides a flexible and user-friendly way to collect participant information at the beginning of an experiment. It creates standardized GUI dialogs that can be customized through configuration files, supporting multiple field types and localization for international studies.
SubInfo solves several common challenges in participant registration:
Standardization: Create consistent participant information forms across experiments
Validation: Automatically validate input based on field constraints
Localization: Display forms in the participant’s language
Configuration: Define forms using YAML or dictionaries for easy modification
Integration: Seamlessly connect with other psyflow components
Key Features¶
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Multiple field types |
Support for string, integer, and choice (dropdown) fields |
Input validation |
Enforce constraints like min/max values and digit length |
Localization |
Display field labels and messages in any language |
YAML configuration |
Define forms using human-readable configuration files |
Automatic defaults |
Add standard fields like subject_id if not specified |
Error handling |
Clear error messages for invalid input |
Quick Reference¶
Purpose |
Method |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Initialize |
|
|
Collect info |
|
|
Access data |
|
|
Validate input |
|
|
Detailed Usage Guide¶
1. Configuring the Form and Collecting Information¶
Option A: Using a YAML Configuration¶
YAML provides a clean, readable way to define your form structure:
# subinfo_config.yaml
subinfo_fields:
- name: subject_id
type: int
constraints:
min: 101
max: 999
digits: 3
- name: age
type: int
constraints:
min: 18
max: 100
- name: gender
type: choice
choices: [Male, Female, Non-binary, Prefer not to say]
- name: handedness
type: choice
choices: [Right, Left, Ambidextrous]
- name: vision
type: choice
choices: [Normal, Corrected-to-normal, Impaired]
# Optional localization mapping
subinfo_mapping:
subject_id: "Participant ID"
age: "Age"
gender: "Gender"
handedness: "Handedness"
vision: "Vision"
Male: "Male"
Female: "Female"
Non-binary: "Non-binary"
Prefer not to say: "Prefer not to say"
Right: "Right"
Left: "Left"
Ambidextrous: "Ambidextrous"
Normal: "Normal"
Corrected-to-normal: "Corrected-to-normal"
Impaired: "Impaired"
registration_successful: "Registration successful!"
registration_failed: "Registration cancelled."
invalid_input: "Invalid input for {field}"
Once you’ve defined your configuration, collecting information is straightforward:
from psyflow import SubInfo
import yaml
# Load configuration from YAML
with open("subinfo_config.yaml", "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
# Create SubInfo instance
subinfo = SubInfo(config)
# Show dialog and collect information
subject_data = subinfo.collect()
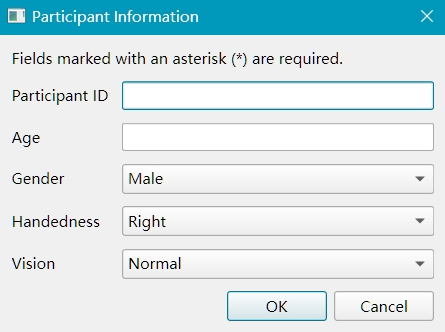
Note
Make sure you used encoding='utf-8' when opening the YAML file to support non-ASCII characters in localization.
Option B: Using a Python Dictionary¶
You can also define the form directly in Python:
config = {
"subinfo_fields": [
{
"name": "subject_id",
"type": "int",
"constraints": {"min": 101, "max": 999, "digits": 3}
},
{
"name": "age",
"type": "int",
"constraints": {"min": 18, "max": 100}
},
{
"name": "gender",
"type": "choice",
"choices": ["Male", "Female", "Non-binary", "Prefer not to say"]
},
{
"name": "handedness",
"type": "choice",
"choices": ["Right", "Left", "Ambidextrous"]
}
],
"subinfo_mapping": {
"subject_id": "Participant ID",
"age": "Age",
"gender": "Gender",
"handedness": "Handedness"
# Add more mappings as needed
}
}
Once you’ve defined your configuration, collecting information is straightforward:
from psyflow import SubInfo
subinfo = SubInfo(config)
# Show dialog and collect information
subject_data = subinfo.collect()
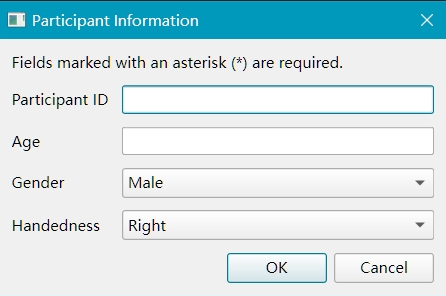
If registration (collection) is failed, the experiment will exit and python enviroment will be closed.
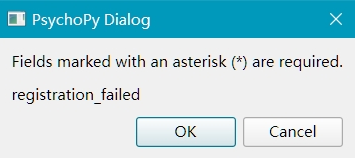
2. Field Types and Constraints¶
SubInfo supports three field types:
String Fields¶
- name: subject_name
type: string
String fields accept any text input without validation.
Integer Fields¶
- name: subject_id
type: int
constraints:
min: 101 # Minimum allowed value
max: 999 # Maximum allowed value
digits: 3 # Required number of digits
Integer fields validate that:
The input can be converted to an integer
The value is within the min/max range (if specified)
The number has exactly the specified number of digits (if specified)
Choice Fields (Dropdowns)¶
- name: condition
type: choice
choices: [Control, Experimental]
Choice fields present a dropdown menu with the specified options.
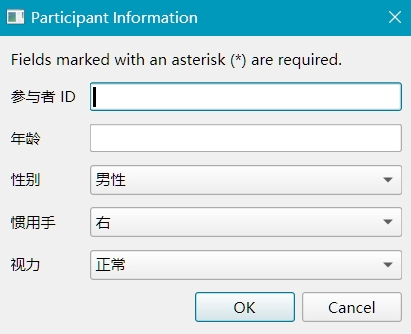
3. Localization¶
For international studies, you can localize the form by providing translations in the subinfo_mapping section:
# Example for subinfo_config.yaml localization
subinfo_mapping:
subject_id: "참가자 ID"
age: "나이"
gender: "성별"
handedness: "주사용 손"
vision: "시력"
Male: "남성"
Female: "여성"
Non-binary: "논바이너리"
Prefer not to say: "응답하지 않음"
Right: "오른손잡이"
Left: "왼손잡이"
Ambidextrous: "양손잡이"
Normal: "정상"
Corrected-to-normal: "교정된 정상"
Impaired: "손상된"
registration_successful: "등록 성공!"
registration_failed: "등록이 취소되었습니다."
invalid_input: "{field}에 대한 잘못된 입력입니다."
from psyflow import SubInfo
import yaml
# Load configuration from YAML
with open("subinfo_config.yaml", "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
# Create SubInfo instance
subinfo = SubInfo(config)
# Show dialog and collect information
subject_data = subinfo.collect()
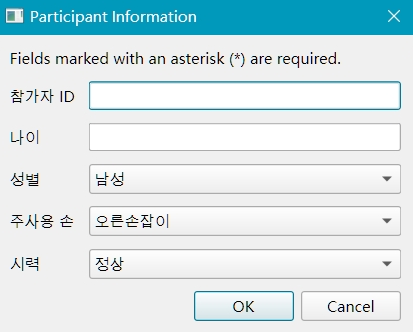
Following same approach, you can do localization for any language by providing the appropriate translations in the subinfo_mapping section.
Tip
In addition to using the chatbox from LLM models for translation,
psyflow has a built-in function (translate_config()) using LLM APIs for translating the subinfo mapping.
Make sure the translations are accurate if you use an LLM to generate them. Consult a native speaker if possible.
4. Add subject information to TaskSettings¶
Once collected, the subject information needs to be passed to TaskSettings to complete the experiment configuration. The information will then be automatically saved together with the other task parameters via TaskSettings.
from psyflow import SubInfo, TaskSettings, load_config
# 1. Load config
cfg = load_config()
# 2. Collect subject info
subform = SubInfo(cfg['subform_config'])
subject_data = subform.collect()
# 3. Load task settings
settings = TaskSettings.from_dict(cfg['task_config'])
settings.add_subinfo(subject_data)
Tip
load_config() is a handy function for loading the configuration stored in config/config.yamlin the default TAPS format.
Next Steps¶
Now that you understand how to use SubInfo, you can:
Learn about TaskSettings for configuring your experiment
Explore StimBank for managing stimuli
Check out BlockUnit for organizing trials into blocks
See StimUnit for creating individual trials